Navigating the financial landscape of an independent school demands precision, foresight, and a clear strategic vision. Without a robust financial framework, even the most well-intentioned educational mission can falter under the weight of unforeseen expenses or mismanaged resources. A well-constructed budget is not merely a document; it is a living blueprint that guides every decision, from staffing ratios to curriculum development, ensuring the school’s long-term health and its ability to deliver on its promise to students and families.
This is where a Private School Operating Budget Template becomes an indispensable tool. It provides a structured, comprehensive approach to financial planning, allowing school leaders, business managers, and finance committees to move beyond guesswork and into a realm of informed decision-making. By systematizing the budgeting process, schools can achieve greater transparency, accountability, and ultimately, a more stable and sustainable future.
The Imperative of Strategic Financial Planning
At its heart, an independent school is a complex organization balancing educational excellence with sound business practices. Financial planning for such an institution goes far beyond simply tracking income and expenses. It involves forecasting, resource allocation aligned with strategic goals, risk management, and ensuring the continued viability of the school’s mission. A thorough operating budget framework serves as the cornerstone of this strategic financial management.
A well-developed financial plan ensures that tuition dollars, donations, and other revenue streams are utilized in the most impactful ways, directly supporting the educational experience. It fosters a culture of fiscal responsibility and allows for proactive responses to economic shifts or unexpected challenges. Without a clear financial roadmap, schools risk making reactive decisions that can detract from their mission and undermine community trust.
Understanding the Core Components of a School Operating Budget
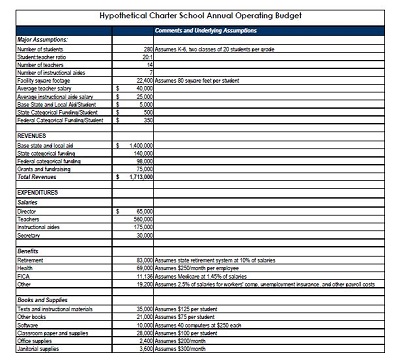
Every independent school, regardless of its size or focus, operates within a set of fundamental financial categories. A comprehensive school operating budget framework typically dissects both revenue and expenditure into manageable, transparent components. Understanding these elements is the first step toward building a robust financial plan.
Revenue Streams often include:
- Tuition and Fees: The primary source of income for most private schools, encompassing tuition, application fees, enrollment deposits, and specific program fees.
- Auxiliary Programs: Revenue generated from extended day programs, summer camps, facility rentals, school stores, and transportation services.
- Contributions and Fundraising: Gifts from individuals, foundations, and corporations, including annual fund donations, capital campaign pledges, and endowment support.
- Investment Income: Returns generated from the school’s endowment or other investment portfolios.
- Government Grants/Support: Depending on the school’s classification and location, certain governmental grants or aid might be available.
Expenditure Categories commonly encompass:
- Salaries and Benefits: The largest component, covering faculty and staff salaries, health insurance, retirement contributions, and other employee benefits.
- Instructional Expenses: Costs directly related to the educational program, such as classroom supplies, textbooks, curriculum development, and professional development for teachers.
- Facilities and Maintenance: Expenses for upkeep, repairs, utilities, cleaning services, landscaping, and property insurance.
- Administrative and Office: Costs associated with the general operation of the school, including administrative salaries, office supplies, technology infrastructure, and legal/accounting fees.
- Marketing and Admissions: Funds allocated for student recruitment, marketing campaigns, open houses, and admissions events.
- Financial Aid: Funds dedicated to scholarships and tuition assistance, essential for maintaining socioeconomic diversity and accessibility.
- Debt Service: Payments on loans or bonds used for capital improvements or other long-term investments.
Benefits of a Structured Budget Approach
Utilizing a structured financial planning tool offers a multitude of advantages that extend beyond mere number crunching. It transforms financial management from a daunting annual task into a strategic, ongoing process.
Firstly, it significantly improves decision-making. With a clear picture of financial inflows and outflows, school leaders can make informed choices about resource allocation, new program investments, and strategic initiatives. This clarity helps in prioritizing needs against available funds, ensuring that decisions are data-driven and align with the school’s mission.
Secondly, it enhances transparency and accountability. A well-defined budget framework clearly outlines where money comes from and where it goes. This transparency builds trust among stakeholders—parents, faculty, staff, and donors—who can see how resources are managed. It also assigns accountability for budget lines, promoting responsible spending throughout the organization.
Thirdly, a comprehensive financial model facilitates proactive financial management. Instead of reacting to financial surprises, schools can anticipate future needs, plan for contingencies, and identify potential challenges before they become crises. This includes planning for enrollment fluctuations, economic downturns, or significant capital expenditures.
Finally, it optimizes resource allocation. By scrutinizing each line item, schools can identify areas of inefficiency or underutilization, allowing them to reallocate funds to areas that will have the greatest impact on student learning and operational effectiveness. This continuous optimization is key to sustainable growth and mission fulfillment.
Crafting Your School’s Financial Blueprint: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing or refining your school’s annual financial plan doesn’t have to be an overwhelming task. By following a systematic approach, you can create a detailed and actionable financial roadmap.
Step 1: Gather Your Data
Begin by collecting all relevant financial information from the previous academic year. This includes actual revenues and expenses, enrollment figures, tuition rates, fundraising results, and any grants received. Historical data provides a crucial baseline for future projections and helps identify trends.
Step 2: Project Revenue Streams
Work with your admissions and advancement teams to project expected enrollment, tuition rates, and anticipated fundraising results for the upcoming year. Be realistic and consider factors like retention rates, new student enrollment goals, and donor giving patterns. Also, factor in income from auxiliary programs and investment returns.
Step 3: Categorize and Estimate Expenses
Go through each expenditure category, estimating costs based on historical data, known contractual obligations (like salaries and benefits), and anticipated changes. Engage department heads in this process to ensure accuracy for their specific areas, such as instructional supplies or technology upgrades. This collaborative approach fosters ownership and more accurate estimates.
Step 4: Allocate and Prioritize
Once initial revenue and expense estimates are in place, compare them. If expenses exceed projected revenues, or if there’s a surplus, engage your leadership team and finance committee to make allocation decisions. This often involves prioritizing expenditures based on strategic goals, mission criticality, and educational impact. This is where a Private School Operating Budget Template truly shines, providing a clear structure to make these critical comparisons.
Step 5: Review, Revise, and Approve
Present the draft budget to key stakeholders, including the finance committee and the full board of trustees. Be prepared to explain assumptions, justifications for major line items, and the strategic rationale behind allocation decisions. Incorporate feedback and make necessary revisions before seeking final approval.
Step 6: Monitor and Adjust
A budget is a living document, not a static one. Throughout the academic year, regularly compare actual financial performance against the approved financial plan. Conduct monthly or quarterly reviews. This ongoing monitoring allows you to identify variances early and make timely adjustments, ensuring the school stays on track or adapts effectively to unforeseen circumstances.
Leveraging Your Budget for Long-Term Sustainability
An annual operating budget is an essential piece of a larger puzzle: the school’s long-term financial sustainability. It should not exist in isolation but rather be intrinsically linked to the institution’s strategic plan and multi-year financial forecasts. By extending the view beyond a single year, schools can better plan for major capital expenditures, endowment growth, and maintaining robust financial reserves.
Connecting the annual financial plan to a multi-year financial roadmap allows for proactive planning for future challenges and opportunities. This foresight might involve building specific reserve funds for facilities maintenance, investing in faculty professional development, or strategically increasing financial aid capacity. A forward-looking approach ensures that today’s financial decisions contribute positively to the school’s enduring mission.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How often should our school’s operating budget be reviewed?
While the annual budget is typically approved once a year, regular reviews are crucial. Most schools conduct monthly or quarterly budget-to-actual comparisons to monitor financial performance and identify variances. A comprehensive review by the finance committee usually happens at least quarterly.
Q2: What’s the biggest challenge schools face in budget management?
One of the primary challenges is managing the balance between increasing costs (especially salaries and benefits, which are often 70-80% of expenses) and the ability to raise tuition or fundraising revenues. Economic fluctuations, enrollment shifts, and unexpected capital needs also pose significant challenges to maintaining fiscal balance.
Q3: Can a small school effectively use a comprehensive budget framework?
Absolutely. Even small schools benefit immensely from a detailed financial plan. While the scale of numbers might differ, the principles of financial planning, revenue projection, expense management, and strategic allocation remain the same. A template simply provides the structure, which can be scaled to fit any size institution.
Q4: How does a budget template adapt to unexpected financial shifts?
A well-designed financial planning tool is inherently flexible. It provides a baseline against which deviations can be measured. When unexpected shifts occur (e.g., lower enrollment, unexpected facility repairs), the template helps identify which budget lines are impacted and allows for quick scenario planning and adjustments, such as reallocating funds or deferring non-essential expenses.
Q5: What role does technology play in modern school budgeting?
Technology plays a transformative role. Accounting software, financial planning platforms, and specialized budgeting tools can automate data entry, generate reports, facilitate scenario modeling, and integrate with other school management systems. This enhances accuracy, efficiency, and the ability to conduct more sophisticated financial analysis.
In the dynamic world of independent education, effective financial stewardship is not just good practice; it’s a necessity for thriving. By adopting a structured approach to your school’s finances, you empower your institution to fulfill its mission, adapt to change, and secure a vibrant future for generations of students. The commitment to meticulous financial planning ultimately translates into a more stable, innovative, and impactful educational environment.
Embracing a comprehensive framework for your school’s finances creates clarity, fosters collaboration, and cultivates a culture of deliberate resource management. It is an investment not just in numbers, but in the sustained excellence of your school’s educational legacy. Taking this strategic step ensures that your school continues to flourish and profoundly impact the lives of its students.