In the intricate world of modern construction, real estate development, and complex commercial projects, relationships often extend beyond the direct parties involved. A developer contracts a builder, who then engages numerous subcontractors. A project financier invests significant capital, and ultimately, an end-purchaser acquires the finished property. While direct contracts govern the primary relationships, a crucial legal gap can emerge when a third party, not directly privy to the initial agreement, needs assurances regarding the quality of work or materials provided by a subcontractor or professional consultant. This is precisely where a collateral warranty agreement template becomes an indispensable tool, creating a direct contractual link and extending duties of care where they otherwise wouldn’t exist.
Understanding the nuances of these multi-party arrangements is critical for mitigating risk, establishing clear lines of accountability, and ensuring legal recourse. For developers, contractors, lenders, purchasers, and legal professionals navigating these complex scenarios, a well-drafted, standardized collateral warranty agreement template offers a streamlined and robust solution. It provides the framework to secure essential protections, clarify obligations, and formalize crucial legal ties, thereby safeguarding investments and fostering greater confidence across all stakeholders involved in a project.
The Imperative for Written Agreements in Modern Business
In today’s fast-paced commercial environment, relying on verbal assurances or implied understandings is a perilous gamble. Projects, especially in sectors like construction and engineering, are growing exponentially in complexity, involving a multitude of parties, specialized services, and significant financial outlays. A clear, comprehensive, and legally binding written agreement serves as the foundational bedrock for all transactions, meticulously outlining each party’s rights, responsibilities, and liabilities.
Without such documentation, disputes can quickly escalate into costly and time-consuming legal battles, eroding trust and jeopardizing project timelines and budgets. Written agreements provide undeniable proof of intent, terms, and conditions, offering clarity and enforceability in a court of law. They serve as a vital reference point, preventing misunderstandings and providing a roadmap for dispute resolution, ultimately fostering greater transparency and accountability among all participants.
Unlocking Protection: Benefits of a Structured Document
Utilizing a well-crafted agreement, such as a collateral warranty agreement template, offers a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond mere administrative convenience. Primarily, it acts as a powerful risk mitigation tool. By establishing a direct contractual link between a warrantor (e.g., a subcontractor or professional) and a beneficiary (e.g., a funder or purchaser), it ensures that the beneficiary has direct recourse for breaches of duty of care, design faults, or defective workmanship that they would otherwise lack.
This structured document provides legal certainty, defining the scope of liability, the duration of the warranty, and specific performance obligations. It saves considerable time and legal fees compared to drafting each agreement from scratch, ensuring consistency across multiple project warranties. Furthermore, it standardizes expectations, facilitates due diligence processes for lenders and purchasers, and ultimately enhances the overall commercial viability and security of a project, fostering confidence among all parties involved.
Adapting the Framework: Customization for Diverse Applications
While the concept of a collateral warranty is perhaps most commonly associated with the construction industry, its underlying principles of establishing third-party contractual links and extending duties of care can be incredibly versatile. A robust collateral warranty agreement template should be designed with this adaptability in mind, allowing for precise customization across a spectrum of industries and unique scenarios.
In construction, for instance, the template can be tailored to specify warranties for structural integrity, mechanical systems, or particular finishes, distinguishing between a developer’s requirements versus a subsequent purchaser’s long-term interests. Beyond construction, analogous agreements might be used in technology licensing, where an end-user needs direct assurances from a software developer, or in complex manufacturing supply chains, where a final product assembler requires a direct warranty from a component supplier. The flexibility lies in adjusting clauses related to scope of work, standards of care, insurance requirements, and assignment rights to reflect the specific risks, regulatory landscape, and commercial realities of each unique application.
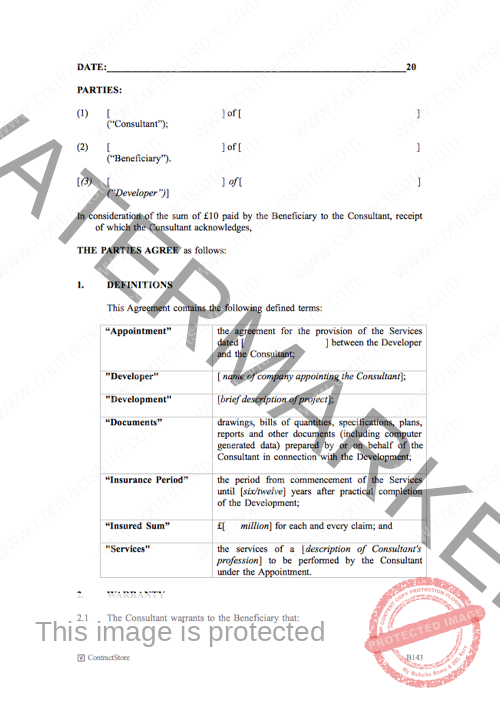
Anatomy of a Robust Collateral Warranty
Every effective collateral warranty agreement template must contain a core set of clauses and sections to ensure it is comprehensive, legally sound, and enforceable. These elements collectively define the scope, obligations, and protections afforded by the agreement.
- Parties: Clearly identifies the warrantor (e.g., contractor, consultant), the beneficiary (e.g., developer, funder, purchaser), and often the original contracting party.
- Recitals: Provides context, outlining the background of the project, the primary contract, and the reason for the collateral warranty.
- Consideration: States the value exchanged (often nominal or tied to the main contract) to make the agreement legally binding.
- Duty of Care: Specifies the standard of care the warrantor must exercise, usually mirroring their obligations under the original contract (e.g., to perform with reasonable skill and care).
- Scope of Warranty/Works: Precisely defines the works, services, or designs covered by the warranty.
- Insurance Requirements: Mandates that the warrantor maintains specific types and levels of insurance (e.g., Professional Indemnity, Public Liability) for the duration of the warranty period.
- Assignment: Outlines under what conditions the beneficiary can assign their rights under the warranty to another party (e.g., a future purchaser of the property).
- Exclusion and Limitation of Liability: Details any caps on liability or specific exclusions, which must be carefully reviewed and negotiated.
- Notice Provisions: Establishes the procedures for notifying parties of claims, breaches, or other significant events.
- Defects Liability Period: Specifies the period during which the warrantor is responsible for rectifying defects.
- Step-in Rights (for Funders): Grants a funder the right to step into the developer’s shoes under the main contract in case of default.
- Dispute Resolution: Specifies the preferred method for resolving disputes (e.g., negotiation, mediation, arbitration, litigation).
- Governing Law and Jurisdiction: Identifies the state or country whose laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of the agreement.
- Entire Agreement Clause: States that the written document constitutes the entire agreement between the parties, superseding prior discussions.
- Severability: Ensures that if one part of the agreement is found unenforceable, the rest remains valid.
- Signatures: Requires authorized signatories from all parties, affirming their acceptance of the terms.
Enhancing Accessibility: Practical Tips for Document Design
Even the most legally robust agreement can fall short if it’s difficult to navigate or understand. Practical considerations for formatting, usability, and readability are paramount, whether the document is intended for print or digital use. A well-designed document reflects professionalism and facilitates clearer communication, minimizing the risk of misinterpretation.
Firstly, employ a clear and consistent layout. Use a legible font (e.g., Arial, Calibri, Times New Roman) in an appropriate size (10-12pt for body text). Ample white space around text and between sections significantly improves readability. Headings and subheadings should be used judiciously to break up dense legal text and provide logical signposts for the reader. Numbered paragraphs or sections allow for easy cross-referencing and discussion. Utilize bullet points or numbered lists for complex items, such as the essential clauses listed above, to present information clearly. Ensure that any definitions of key terms are grouped together in a dedicated section at the beginning or clearly referenced throughout. For digital use, consider using internal links or a table of contents to aid navigation. Finally, strive for plain language where possible, avoiding overly convoluted legal jargon without sacrificing precision, ensuring that all parties can comprehend their obligations and rights.
The strategic deployment of a comprehensive collateral warranty agreement template is more than just a legal formality; it’s a fundamental aspect of sound project management and risk control in multi-party undertakings. By providing a clear, standardized framework, it empowers all stakeholders to navigate complex relationships with confidence, ensuring that duties of care are appropriately extended and liabilities are clearly defined.
Ultimately, opting for a meticulously developed collateral warranty agreement template translates into significant efficiencies and peace of mind. It allows businesses and legal professionals to swiftly generate vital contractual documents that are both legally robust and easily customizable, thereby minimizing drafting time and reducing potential legal exposure. In an environment where precision and accountability are paramount, this type of professional solution is not just an advantage—it’s an absolute necessity for securing successful project outcomes and fostering enduring trust among all participants.