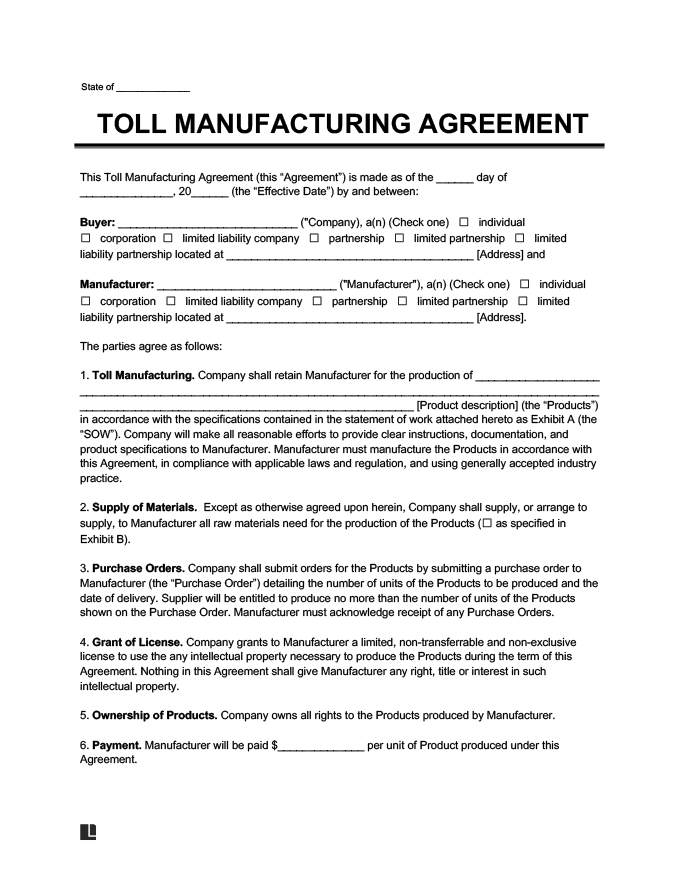
In the dynamic landscape of modern commerce, businesses frequently seek specialized expertise and cost efficiencies by outsourcing various aspects of their operations. One increasingly common practice is toll manufacturing, where a company provides its raw materials or components to another manufacturer, who then processes them into finished goods or intermediate products for a fee, known as a "toll." This arrangement allows businesses to leverage specialized equipment, skilled labor, and production capacity without significant capital investment in their own facilities.
Establishing a clear, legally sound foundation for such a partnership is not merely a best practice; it is an absolute necessity. A well-crafted toll manufacturing agreement serves as the bedrock of this relationship, defining expectations, outlining obligations, and mitigating potential risks for both the outsourcing company and the contract manufacturer. For any business engaged in or considering this model, understanding the structure and importance of a robust toll manufacturing agreement template is crucial for successful and compliant operations.
The Indispensable Value of a Formal Contract
In an era defined by complex supply chains and stringent regulatory requirements, relying on verbal agreements or informal understandings is a recipe for potential disputes and financial losses. A formal, written contract provides clarity, reduces ambiguity, and establishes a legally binding framework that protects all parties involved. It serves as a single source of truth for the entire manufacturing process, from material reception to final product delivery.
Today’s business environment demands precision and accountability. Without a detailed agreement, misunderstandings can quickly escalate into costly legal battles, damage business relationships, and disrupt production schedules. A comprehensive written document ensures that both the "principal" (the company providing materials) and the "toll manufacturer" clearly understand their roles, responsibilities, and the specific terms governing their collaboration. This proactive approach minimizes risks and fosters a foundation of trust.
Safeguarding Your Interests: Key Benefits and Protections
Utilizing a well-structured document, such as a toll manufacturing agreement template, offers numerous benefits that extend far beyond simple legal protection. It standardizes critical operational procedures, ensuring consistency and quality across all production runs. This leads to greater efficiency and predictability in the manufacturing process.
The protections afforded by such an agreement are invaluable. It shields both parties from unforeseen circumstances, clarifies liability for defects or delays, and establishes mechanisms for dispute resolution. For the principal, it safeguards their intellectual property, product specifications, and proprietary processes. For the manufacturer, it defines payment terms, service expectations, and limitations of liability, ensuring fair compensation and protection against unreasonable demands. Having a solid toll manufacturing agreement template in place is a proactive step towards securing a mutually beneficial and legally sound partnership.
Tailoring Your Agreement: Customization for Diverse Needs
While a standardized agreement template provides an excellent starting point, its true value lies in its adaptability. Toll manufacturing arrangements vary widely across industries—from pharmaceuticals and food processing to electronics and consumer goods—each with unique regulatory demands, material handling requirements, and production complexities. Therefore, the ability to customize the core document is paramount.
A versatile template can be adjusted to reflect specific industry standards, product specifications, and operational workflows. For instance, an agreement for pharmaceutical toll manufacturing would require stringent clauses on GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), regulatory compliance, and batch traceability, which might differ significantly from an agreement for manufacturing plastic components. Understanding how to modify the core provisions ensures the contract accurately represents the unique facets of each business relationship and project.
Anatomy of a Robust Agreement: Essential Clauses
A comprehensive toll manufacturing agreement must address all critical aspects of the relationship to prevent ambiguity and ensure smooth operations. The following clauses are typically essential:
- Parties and Recitals: Clearly identifies the principal and the manufacturer, including their legal names and addresses. Recitals provide background context for the agreement.
- Scope of Services/Work: Detailed description of the manufacturing services to be provided, including specific products, processes, and any ancillary services like packaging or labeling.
- Material Supply and Ownership: Specifies how raw materials will be supplied by the principal, who bears the cost and risk of transport, and clarifies that ownership of the materials and finished products remains with the principal.
- Product Specifications and Quality Control: Outlines the precise technical specifications, quality standards, and testing procedures the finished products must meet. It also defines inspection rights and defect resolution processes.
- Pricing and Payment Terms: Clearly states the "toll fee" per unit or batch, payment schedule, invoicing procedures, and any provisions for price adjustments.
- Term and Termination: Defines the duration of the agreement and the conditions under which either party can terminate it, including cure periods for breaches.
- Confidentiality: A robust clause protecting proprietary information, trade secrets, and any data exchanged between the parties during the course of the agreement.
- Intellectual Property (IP): Clarifies that the principal retains ownership of all IP related to the product and processes, and that the manufacturer does not gain any rights to it.
- Indemnification and Limitation of Liability: Establishes which party is responsible for specific types of losses, damages, or claims, and sets limits on financial liability.
- Representations and Warranties: Statements by each party affirming certain facts (e.g., legal capacity to enter the agreement, compliance with laws) and guaranteeing the quality of services or materials.
- Insurance: Requirements for each party to maintain appropriate insurance coverage (e.g., general liability, product liability).
- Compliance with Laws: A mutual commitment to adhere to all applicable local, state, and federal laws and regulations relevant to the manufacturing process.
- Force Majeure: Provisions addressing unforeseen events beyond the parties’ control that may impact performance (e.g., natural disasters, war).
- Dispute Resolution: Outlines the process for resolving disagreements, such as negotiation, mediation, or arbitration, before resorting to litigation.
- Governing Law and Jurisdiction: Specifies which state’s laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of the agreement, and where any legal actions would be filed.
- Notices: Defines how formal communications between the parties should be delivered.
- Entire Agreement: States that the written contract constitutes the entire agreement between the parties, superseding all prior discussions or understandings.
- Amendments: Specifies that any changes to the agreement must be in writing and signed by both parties.
- Assignment: Clarifies whether either party can transfer their rights or obligations under the agreement to a third party.
Beyond the Legalities: Practical Tips for Document Design
While the legal content of a contract is paramount, its practical usability and readability significantly impact its effectiveness. A well-designed agreement is easy to navigate, understand, and reference, whether it’s for print or digital use. Consider these practical tips to enhance the document’s utility.
Employ clear, concise language, avoiding excessive legal jargon where simpler terms suffice. Use consistent formatting throughout, including headings, subheadings, and bullet points, to break up large blocks of text and improve scannability. A table of contents at the beginning can be immensely helpful for quick navigation, especially in longer documents. Ensure proper paragraph spacing and font choices that are easy on the eyes. For digital use, consider hyperlinking to definitions or related sections within the document. Finally, a clean layout with adequate margins makes the document professional and user-friendly, encouraging thorough review and understanding by all stakeholders.
The journey of bringing a product to market is fraught with complexities, and outsourcing manufacturing can introduce an additional layer of challenge if not properly managed. A meticulously drafted agreement is not just a formality; it is an essential risk management tool that provides clarity, protection, and a framework for successful collaboration between a principal and a toll manufacturer. It is the blueprint for a productive relationship, ensuring that both parties are aligned on expectations and responsibilities.
By leveraging a comprehensive toll manufacturing agreement template, businesses can save significant time and legal costs that would otherwise be spent drafting a contract from scratch. It empowers them to enter into partnerships with confidence, knowing that their interests are protected and their operational guidelines are clearly defined. In today’s competitive landscape, such a professional, time-saving solution is an invaluable asset for any company engaged in outsourced production.