Introduction
So, you’ve got a brilliant idea for a project and you’re ready to pitch it. But before you unleash your creativity on unsuspecting clients or colleagues, you need a solid foundation – a well-structured project proposal. This document is your roadmap, your sales pitch, and your contract all rolled into one. Think of it as your first impression, and you want to make it count!
What is a Project Proposal?
In the simplest terms, a project proposal is a formal document that outlines a proposed project. It’s your chance to convince others (like clients, investors, or your boss) that your project is worthwhile and deserves their time, money, and resources.
Why is a Project Proposal Important?
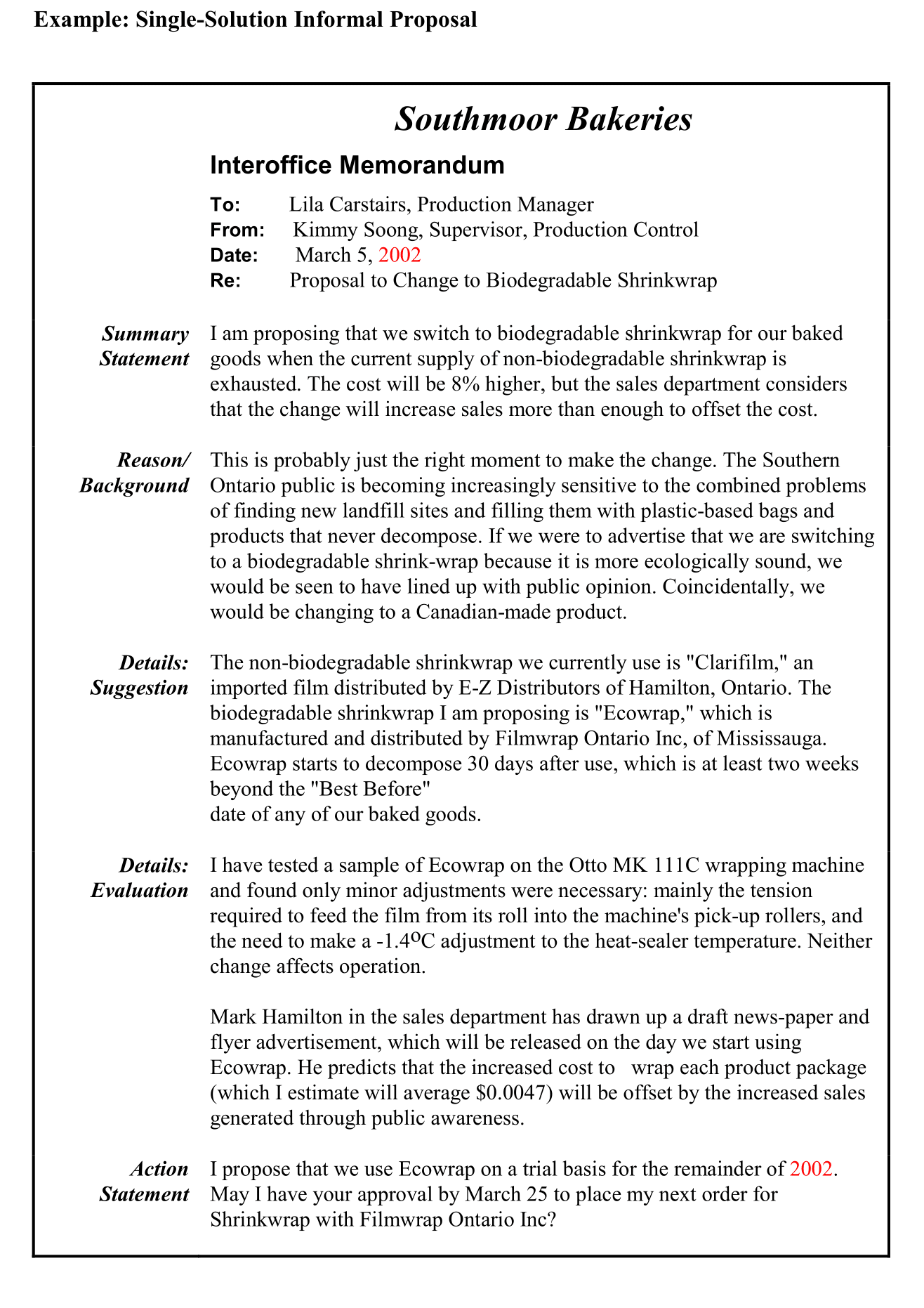
Image Source: niftypm.com
Clarity and Focus: A well-written proposal helps you clarify your project goals, objectives, and the steps involved. This clarity ensures everyone is on the same page from the start, minimizing confusion and potential roadblocks down the line.
Key Components of a Project Proposal
A typical project proposal includes the following sections:
1. Executive Summary
This is your elevator pitch – a concise overview of the entire proposal.
2. Project Introduction
Provide background information on the project.
3. Project Objectives
Clearly state the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives of the project.
4. Project Methodology
Describe the approach you will take to achieve the project objectives.
5. Project Team
Introduce the team members who will be working on the project.
6. Project Budget
Provide a detailed budget breakdown, including all anticipated costs such as:
7. Project Timeline
Create a realistic timeline for the project, including key milestones and deadlines.
8. Evaluation Plan
Describe how you will measure the success of the project.
9. Conclusion
Briefly summarize the key benefits of the project and reiterate its importance.
Tips for Writing an Effective Project Proposal
Know Your Audience: Tailor your proposal to the specific needs and interests of your audience.
Project Proposal Format Sample
To help you visualize these components, here’s a simple project proposal format sample:
[Project Title]
Conclusion
Crafting a compelling project proposal takes time and effort, but it’s a crucial step in the project lifecycle. By following these guidelines and using the provided format sample as a starting point, you can create a professional and persuasive document that increases your chances of securing approval and successfully bringing your project to fruition.
FAQs
1. What is the ideal length for a project proposal?
The length of a project proposal can vary depending on the complexity and scope of the project. However, a good rule of thumb is to keep it concise and focused. Aim for a length of 5-15 pages for most projects.
2. Can I use templates for my project proposals?
Yes, using templates can save you time and ensure consistency in your formatting. Many word processing software programs, such as Microsoft Word, offer pre-designed project proposal templates. You can also find numerous free templates online.
3. How do I ensure my project proposal is persuasive?
Focus on the benefits of your project and how it will address a specific need or opportunity. Use strong evidence, such as data, research findings, and case studies, to support your claims.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid in project proposals?
Poorly defined objectives: Vague or unrealistic objectives can weaken your proposal.
5. How can I track the progress of my project against the proposal?
Regularly review the project plan and compare it to actual progress. Use project management tools, such as Gantt charts and progress reports, to monitor key milestones and identify any potential roadblocks.
Remember, a well-written project proposal is an essential tool for successful project management. By following these guidelines and putting in the necessary effort, you can increase your chances of achieving your project goals and making a lasting impact.
Project Proposal Format Sample