In the complex landscape of modern enterprises, individual business units often operate as self-contained entities, each with its own goals, challenges, and financial imperatives. Managing these diverse operational segments effectively requires precision, foresight, and a clear financial strategy. A well-crafted budget isn’t just a spreadsheet; it’s a strategic roadmap that translates operational objectives into financial terms, guiding resource allocation and performance measurement for each distinct part of the organization.
For unit leaders and financial stakeholders, the process of developing a comprehensive financial plan can be daunting without a structured approach. That’s where a standardized financial planning guide for departments becomes indispensable. It provides a common language and framework, ensuring consistency across the enterprise while allowing for the unique nuances of each unit. This foundational document empowers teams to take ownership of their financial health, fostering accountability and contributing directly to the overarching success of the company.
Why a Dedicated Budgeting Tool Matters for Your Unit
Each business unit, whether it’s a marketing department, a product development team, or a sales division, has distinct revenue streams, expense categories, and operational rhythms. Relying on a generic corporate budget format can often overlook these critical specificities, leading to inaccuracies and misallocated resources. A tailored departmental budget framework addresses these challenges head-on, providing a dedicated structure that aligns with the unit’s specific operational needs and strategic objectives.
Implementing a robust business unit budgeting tool provides unparalleled clarity. It forces teams to meticulously evaluate their spending, project revenue, and anticipate capital needs, leading to more informed decision-making. This focused approach reduces the likelihood of financial surprises and helps leadership proactively identify potential risks or opportunities. Ultimately, it transforms budgeting from a mere compliance exercise into a powerful strategic planning instrument.
Key Benefits of a Structured Budgeting Framework
Adopting a specialized budget worksheet for individual units offers a multitude of advantages that extend beyond simple financial tracking. It cultivates a culture of fiscal responsibility and empowers teams with the data needed to make impactful decisions. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
- **Enhanced Financial Clarity:** Provides a transparent view of the unit’s **financial health**, making it easier to understand where money comes from and where it goes.
- **Improved Resource Allocation:** Allows for strategic distribution of funds to areas that will yield the **highest return** or are critical to the unit’s mission.
- **Better Decision-Making:** Equips unit leaders with reliable financial data to make **informed choices** about projects, hiring, and investments.
- **Increased Accountability:** Clearly defines financial targets and responsibilities, fostering a greater sense of **ownership among teams**.
- **Performance Measurement:** Establishes benchmarks against which the unit’s actual financial performance can be **measured and evaluated**.
- **Strategic Alignment:** Ensures that the unit’s financial plans are **consistent with** and contribute to the broader organizational goals.
- **Risk Mitigation:** Helps in identifying potential financial shortfalls or excesses **early on**, allowing for timely corrective actions.
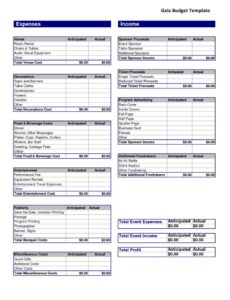
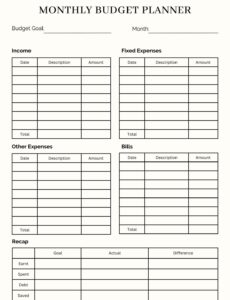
Essential Components of an Effective Unit Budget
A comprehensive operational budget blueprint isn’t just about listing numbers; it’s about categorizing them logically to provide meaningful insights. Understanding the key sections that constitute a robust budget allows for a more accurate and actionable financial plan. Each component plays a vital role in painting a complete picture of the unit’s financial landscape.
Typically, a well-designed financial planning document for departments will include detailed sections for various financial elements. This granularity ensures that no critical aspect of the unit’s operations is overlooked, from daily expenses to long-term investments. Breaking down the budget into these core components facilitates easier analysis, forecasting, and ongoing management.
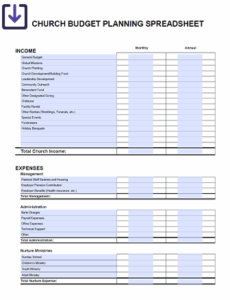
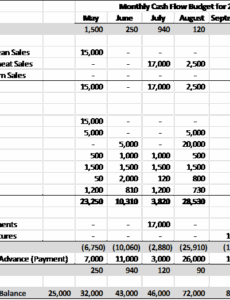
Revenue Projections
This section outlines all anticipated income sources for the business unit. Depending on the unit, this could include sales of specific products or services, inter-departmental charges, or allocated corporate funding. Accurate revenue forecasting is crucial as it forms the basis for all spending decisions. It requires careful consideration of historical data, market trends, and any planned initiatives that could impact income.
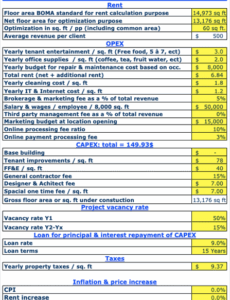
Operating Expenses
These are the costs associated with the day-to-day running of the business unit. This broad category typically includes:
- **Personnel Costs:** Salaries, wages, benefits, and payroll taxes for all employees within the unit. Often the largest expense, requiring careful planning.
- **Marketing & Sales Expenses:** Advertising, promotional activities, travel for sales teams, and related costs.
- **Office & Administrative:** Rent (if separately accounted for), utilities, office supplies, software subscriptions, and general administrative overhead.
- **Travel & Entertainment:** Costs associated with business trips, client meetings, and team events.
- **Professional Services:** Fees paid to external consultants, legal services, or specialized contractors.
Capital Expenditures (CapEx)
Capital expenditures refer to funds used by a company to acquire, upgrade, and maintain physical assets such as property, industrial buildings, or equipment. For a business unit, this might include new computer hardware, specialized machinery, or significant software licenses with a lifespan of more than one year. These are typically larger, one-time investments that are amortized over time.
Variance Analysis & Contingency
A robust budget also includes a plan for analyzing variances between actual and budgeted figures, and a contingency fund. The contingency allocation accounts for unforeseen expenses or shifts in economic conditions, providing a buffer against financial shocks. Regular variance analysis helps in understanding performance deviations and making necessary adjustments throughout the fiscal period.
Crafting Your Unit’s Financial Roadmap: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing an effective Business Unit Budget Template isn’t a one-time task; it’s an iterative process that requires careful planning, collaboration, and a commitment to accuracy. The steps outlined below provide a practical approach to building a financial plan that truly serves your unit’s strategic goals. Engaging key stakeholders throughout this journey ensures buy-in and a more realistic outcome.
Step 1: Gather Historical Data and Strategic Goals
Begin by compiling past financial performance data for your unit. Look at previous years’ budgets, actual spending, and revenue generation. Simultaneously, review the unit’s current strategic objectives and upcoming initiatives. What are the key projects planned? Are there new hires anticipated? Understanding both history and future direction is foundational.
Step 2: Project Revenue and Income
Based on historical trends, market forecasts, and strategic initiatives, estimate all potential income streams for the upcoming period. Be realistic yet ambitious. Consider different scenarios (optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely) to build flexibility into your projections. This section provides the fuel for all subsequent spending decisions.
Step 3: Detail Operating Expenses
Work through each category of operating expenses. For recurring costs like salaries or software subscriptions, use current rates and planned changes. For variable costs, such as marketing campaigns or project-specific supplies, estimate based on planned activities and historical averages. Be thorough and account for even small expenditures, as they can add up quickly.
Step 4: Plan Capital Expenditures
Identify any significant assets or upgrades required for the unit during the budget period. Document the expected cost, the business justification, and the timing of these expenditures. Remember that CapEx items typically undergo a separate approval process due to their scale and long-term impact.
Step 5: Review, Refine, and Allocate Contingency
Once initial figures are compiled, review them critically. Are the revenue projections attainable? Are expenses justified and efficient? Look for areas where costs can be reduced without compromising performance. Allocate a reasonable contingency fund (typically 5-10% of total expenses) to cover unforeseen circumstances.
Step 6: Seek Approval and Communicate
Present your refined budget to relevant stakeholders and upper management for feedback and final approval. Be prepared to explain your assumptions and justifications. Once approved, clearly communicate the budget to your team, emphasizing their role in adhering to the financial plan. This fosters transparency and shared responsibility.
Customization and Best Practices for Your Business Unit’s Budget
While a Business Unit Budget Template provides a solid starting point, its true power lies in its adaptability. No two business units are exactly alike, and therefore, a financial plan must be tailored to reflect the unique operational environment, market dynamics, and strategic priorities of each specific segment. Effective customization transforms a generic framework into a dynamic tool that directly addresses the unit’s needs.
Beyond mere adaptation, adhering to best practices ensures the longevity and effectiveness of your unit financial planning document. These practices promote accuracy, foster collaboration, and integrate the budgeting process seamlessly into the unit’s ongoing operations. A well-maintained and thoughtfully customized budget becomes a living document, evolving with the unit it serves.
Tailoring the Categories
If your unit has unique expense categories (e.g., specific research grants, specialized equipment maintenance), ensure the template allows for these. Conversely, if certain categories are irrelevant, consider removing or consolidating them to avoid unnecessary complexity. The goal is to create a segment budget management tool that is comprehensive yet intuitive for your team.
Forecasting with Scenario Planning
Don’t just create one forecast; develop multiple scenarios (best-case, worst-case, most likely). This provides a more robust financial plan that can withstand various market conditions or operational shifts. Scenario planning enhances agility and prepares your unit for potential challenges or opportunities.
Promote Collaboration
Involve key team members from different functions within your unit in the budgeting process. Their input can provide valuable insights into operational costs and potential revenue streams, increasing the accuracy and buy-in of the final budget. A collaborative approach makes the budget a shared responsibility, not just a finance department mandate.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
A budget is not static. Regularly compare actual financial performance against your budgeted figures. Implement quarterly or even monthly reviews to identify variances promptly. This allows for timely adjustments and course corrections, ensuring that your comprehensive budgeting tool remains relevant throughout the fiscal year.
Leverage Technology
Utilize budgeting software or advanced spreadsheet functions to automate calculations, track progress, and generate reports. Technology can significantly streamline the annual unit budget process, reduce errors, and free up time for more strategic analysis.
Beyond the Numbers: Strategic Implications
The strategic financial plan for business segments extends far beyond mere accounting. It is a powerful instrument for strategic alignment, fostering a deeper understanding of how day-to-day operations contribute to the larger organizational vision. When a unit’s financial plan is meticulously crafted and thoughtfully executed, it becomes a testament to its commitment to fiscal health and strategic growth.
By providing a clear financial blueprint, this document enables unit leaders to articulate their resource needs effectively, justify investments, and measure the impact of their initiatives. It empowers them to proactively manage their financial destiny, driving innovation and efficiency that ultimately propels the entire enterprise forward. The investment in a structured budget document is an investment in strategic foresight and operational excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between a business unit budget and a corporate budget?
A business unit budget focuses on the specific financial details, revenues, and expenses of an individual department or operational segment within a larger company. In contrast, a corporate budget consolidates all these individual unit budgets, along with corporate-level overheads and revenues, to provide an overall financial plan for the entire organization.
How frequently should a business unit budget be reviewed or revised?
While most business units create an annual budget, it’s best practice to review it monthly or quarterly. This allows unit leaders to track performance against the plan, identify significant variances, and make necessary adjustments due to unforeseen circumstances or shifts in market conditions. A mid-year revision is common for major strategic shifts.
Is a budget template suitable for highly variable revenue units?
Absolutely. For units with highly variable revenue, a budget template is even more critical. It encourages scenario planning (best-case, worst-case, most likely) and helps establish a baseline for expenses, ensuring the unit can maintain operations even during leaner periods. It also highlights the need for robust contingency planning.
What role does collaboration play in creating an effective unit budget?
Collaboration is vital. Involving key team members from various functions within the business unit in the budgeting process ensures that all operational needs and potential revenue streams are accurately represented. This fosters a sense of ownership, increases buy-in, and leads to a more realistic and achievable financial plan for the unit.
Crafting a robust financial blueprint for your business unit is more than just an annual chore; it’s a foundational act of strategic management. By leveraging a well-designed financial allocation model, you equip your team with the clarity, discipline, and foresight necessary to navigate financial complexities and seize opportunities. It transforms abstract goals into actionable financial targets, aligning daily operations with long-term vision.
Embrace the power of a structured financial plan. It will not only streamline your financial processes but also empower your unit to operate with greater agility, accountability, and ultimately, greater success. Invest the time in building a precise and adaptable budget, and watch as your business unit transforms its financial potential into tangible growth and sustained achievement.