A pay stub, also known as an earnings statement, is a crucial document that provides a detailed breakdown of your earnings and deductions for a specific pay period. While employers typically provide these, understanding the components of a pay stub can be beneficial for various reasons, such as tracking your income, verifying employment, and ensuring accurate tax filings.
This guide will walk you through the common elements found on a blank pay stub form, explaining their significance and how they contribute to your overall compensation.
1. Employee Information
Employee Name: This section clearly identifies the recipient of the pay stub.
2. Pay Period Information
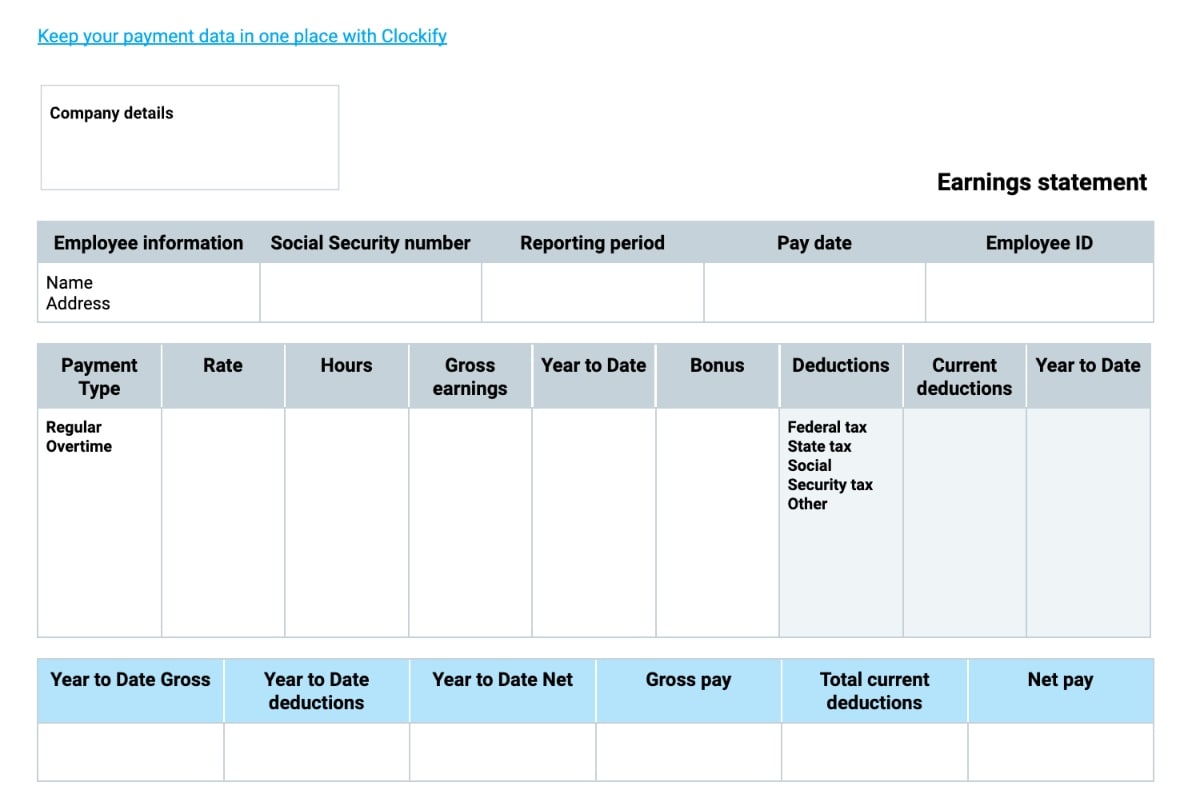
Image Source: clockify.me
Pay Period Dates: Indicates the start and end dates of the pay period covered by the stub.
3. Gross Earnings
Regular Pay: The standard amount earned for the regular hours worked.
4. Deductions
Federal Income Tax: Withheld from your paycheck to fund federal government programs.
5. Net Pay
6. Year-to-Date (YTD) Information
YTD Gross Earnings: The total amount earned by the employee from the beginning of the year to the end of the pay period.
Understanding Your Pay Stub
Reviewing your pay stub regularly can help you:
Track your income and expenses: Monitor your earnings and deductions to ensure they are accurate and to better manage your budget.
By understanding the information on your pay stub, you can gain a better understanding of your finances and make informed decisions about your income and expenses.
Conclusion
A pay stub is a valuable document that provides a detailed record of your earnings and deductions. By familiarizing yourself with the components of a pay stub and reviewing it regularly, you can ensure the accuracy of your pay and make informed financial decisions.
FAQs
What happens if there are errors on my pay stub?
If you notice any errors on your pay stub, such as incorrect deductions or missing earnings, contact your payroll department immediately. They can investigate the issue and make the necessary corrections.
Can I get a copy of my pay stub if I lose it?
Yes, you can usually obtain a copy of your pay stub from your employer. Contact your payroll department or HR department to request a duplicate. Some employers may also provide access to pay stubs through an employee portal.
What should I do if I have questions about my pay stub?
If you have any questions about your pay stub, don’t hesitate to contact your payroll department. They are there to assist you with any inquiries you may have.
How long should I keep my pay stubs?
It is generally recommended to keep pay stubs for at least seven years for tax purposes. However, it is advisable to consult with a tax professional for specific guidance on record retention requirements.
Can I use my pay stub as proof of income?
Yes, pay stubs can often be used as proof of income for various purposes, such as applying for loans, renting an apartment, or enrolling in certain programs.
This article provides a basic overview of a blank pay stub form. Please note that the specific information and format of pay stubs may vary depending on the employer and the applicable laws and regulations.
Blank Pay Stub Form